True-breeding- term used to describe organisms that produce offspring identicle to themselves if allowed to self pollinate. http://www.sparknotes.com/testprep/books/sat2/biology/chapter7section3.rhtml Trait- specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/genpsytraits.html
Trait- specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/genpsytraits.html

Gene- A hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism. Genes undergo mutation when their DNA sequence changes.http://www.kidshealth.org/kid/talk/qa/what_is_gene.html
 Trait- specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/genpsytraits.html
Trait- specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. http://webspace.ship.edu/cgboer/genpsytraits.html
Gene- A hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism. Genes undergo mutation when their DNA sequence changes.http://www.kidshealth.org/kid/talk/qa/what_is_gene.html
Allele- any of several forms of a gene, usually arising through mutation, that are responsible for hereditary variation. http://images.google.com/imgresimgurl=http://www.genome.gov/Pages/Hyperion/DIR/VIP/Glossary/Illustration/Images/allele.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.dadamo.com/wiki/wiki.pl/Allele&h=251&w=496&sz=36&hl=en&start=7&um=1&tbnid=5v9pTPKCBoJ6sM:&tbnh=66&tbnw=130&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dallele%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26safe%3Doff Gamete- A reproductive cell having the haploid number of chromosomes, especially a mature sperm or egg capable of fusing with a gamete of the opposite sex to produce the fertilized egg.http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.scienceaid.co.uk/biology/genetics2/images/gametes.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.scienceaid.co.uk/biology/genetics2/meiosis.html&h=350&w=561&sz=44&hl=en&start=13&um=1&tbnid=ikHSdTy7HgV7iM:&tbnh=83&tbnw=133&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dgamete%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26safe%3Doff
Gamete- A reproductive cell having the haploid number of chromosomes, especially a mature sperm or egg capable of fusing with a gamete of the opposite sex to produce the fertilized egg.http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.scienceaid.co.uk/biology/genetics2/images/gametes.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.scienceaid.co.uk/biology/genetics2/meiosis.html&h=350&w=561&sz=44&hl=en&start=13&um=1&tbnid=ikHSdTy7HgV7iM:&tbnh=83&tbnw=133&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dgamete%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26safe%3Doff
 Gamete- A reproductive cell having the haploid number of chromosomes, especially a mature sperm or egg capable of fusing with a gamete of the opposite sex to produce the fertilized egg.http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.scienceaid.co.uk/biology/genetics2/images/gametes.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.scienceaid.co.uk/biology/genetics2/meiosis.html&h=350&w=561&sz=44&hl=en&start=13&um=1&tbnid=ikHSdTy7HgV7iM:&tbnh=83&tbnw=133&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dgamete%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26safe%3Doff
Gamete- A reproductive cell having the haploid number of chromosomes, especially a mature sperm or egg capable of fusing with a gamete of the opposite sex to produce the fertilized egg.http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.scienceaid.co.uk/biology/genetics2/images/gametes.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.scienceaid.co.uk/biology/genetics2/meiosis.html&h=350&w=561&sz=44&hl=en&start=13&um=1&tbnid=ikHSdTy7HgV7iM:&tbnh=83&tbnw=133&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dgamete%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26safe%3Doff Probability- likelyhood that a particulat event will occur. http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://staff.jccc.net/pdecell/transgenetics/treeprob.gif&imgrefurl=http://staff.jccc.net/pdecell/transgenetics/probability.html&h=345&w=334&sz=5&hl=en&start=1&um=1&tbnid=eso4jlhSTMNX1M:&tbnh=120&tbnw=116&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dprobability%2Bgenetics%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26safe%3Doff
Probability- likelyhood that a particulat event will occur. http://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://staff.jccc.net/pdecell/transgenetics/treeprob.gif&imgrefurl=http://staff.jccc.net/pdecell/transgenetics/probability.html&h=345&w=334&sz=5&hl=en&start=1&um=1&tbnid=eso4jlhSTMNX1M:&tbnh=120&tbnw=116&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dprobability%2Bgenetics%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26safe%3Doff Punnett Square- diagram showing the gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross. http://users.adelphia.net/~lubehawk/BioHELP!/psquare.htm
Punnett Square- diagram showing the gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross. http://users.adelphia.net/~lubehawk/BioHELP!/psquare.htmHomozygous- having identical pairs of genes for any given pair of hereditary characteristics. http://biology.about.com/od/geneticsglossary/g/homozygous.htm

Heterozygous- Having different alleles at one or more corresponding chromosomal loci. http://biology.about.com/od/geneticsglossary/g/heterozygous.htm

Phenotype- the appearance of an organism resulting from the interaction of the genotype and the environment. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Genotype-phenotype_distinction

Genotype- the genetic makeup of an organism or group of organisms with reference to a single trait, set of traits, or an entire complex of traits. http://www.iscid.org/encyclopedia/Genotype
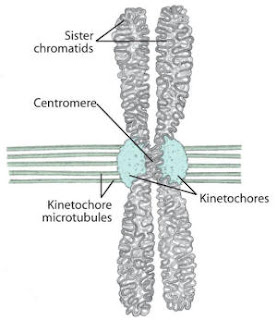
 Homologous- having the same alleles or genes in the same order of arrangement: homologous chromosomes. http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Homologous_chromosome
Homologous- having the same alleles or genes in the same order of arrangement: homologous chromosomes. http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Homologous_chromosome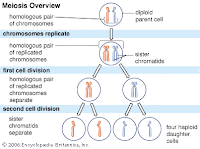
Diploid- having two similar complements of chromosomes. http://biology.plosjournals.org/perlserv/?request=get-document&doi=10.1371%2Fjournal.pbio.0050254&ct=1


Meiosis- part of the process of gamete formation, consisting of chromosome conjugation and two cell divisions, in the course of which the diploid chromosome number becomes reduced to the haploid. http://youtube.com/watch?v=D1_-mQS_FZ0

Tetrad- a group of four chromatids formed by synapsis at the beginning of meiosis. http://www.contexo.info/DNA_Basics/images/mimovchanged2.gif

Crossing-Over- The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes that occurs during meiosis and contributes to genetic variability. http://youtube.com/watch?v=ngmL8T3Hfg8